Unbelievable Info About What Is A Linear Smoother Tableau Combine Line And Bar Chart

Smoothing is a very powerful technique used all across data analysis.
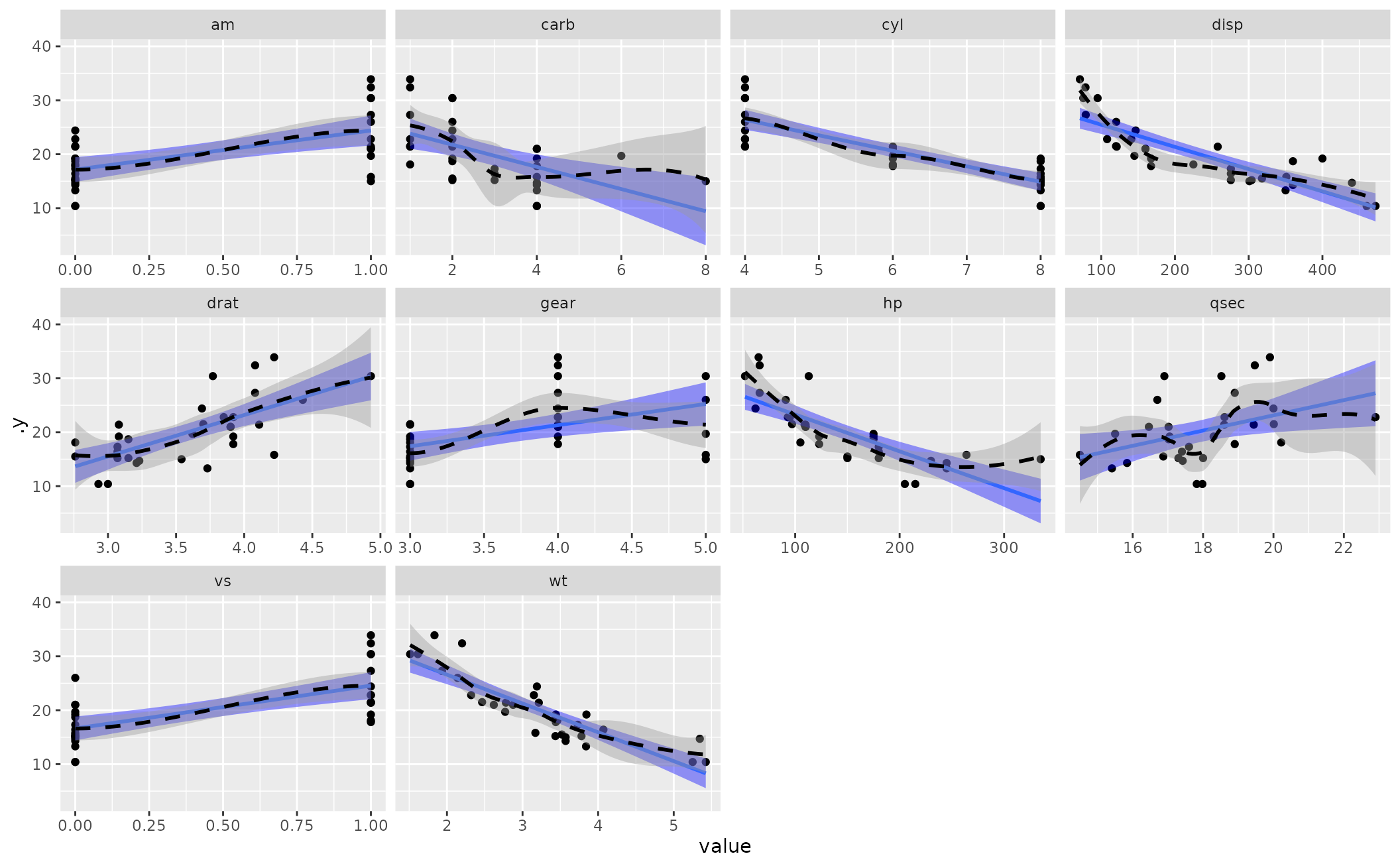
What is a linear smoother. The case is considered that s s is an ordered linear smoother according to some easily interpretable, qualitative conditions. Generally smooth out the irregular roughness to see a clearer signal. It is designed to detect trends in.
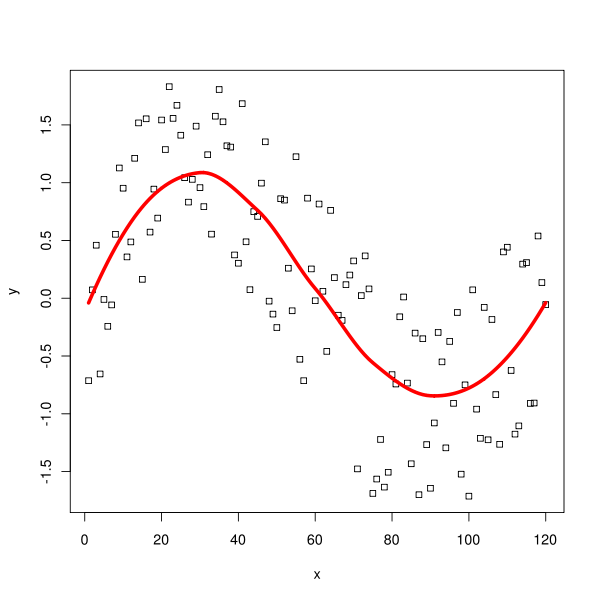
Lowess (locally weighted scatterplot smoothing), sometimes called loess (locally weighted smoothing), is a popular tool used in regression analysis that creates a smooth. Insanely fast smoothing and interpolation in just a few lines of python or. To come up with a way of visualizing relationships between two variables without resorting to a regression lines, statisticians and mathematicians have developed techniques for.
In this section, some of the most common smoothing methods are introduced and discussed. We focus on scatterplot smooths, for which p = 1. In a few lines of code, the method provides quick and reliable smoothing with inbuilt interpolation that can handle large stretches of missing data.
Though noisier, the same might be said of economic fluctuations, which aggregate the activity of. In that case our predictive model is, or becomes, our smoother. Take it to the next level with gear that is.
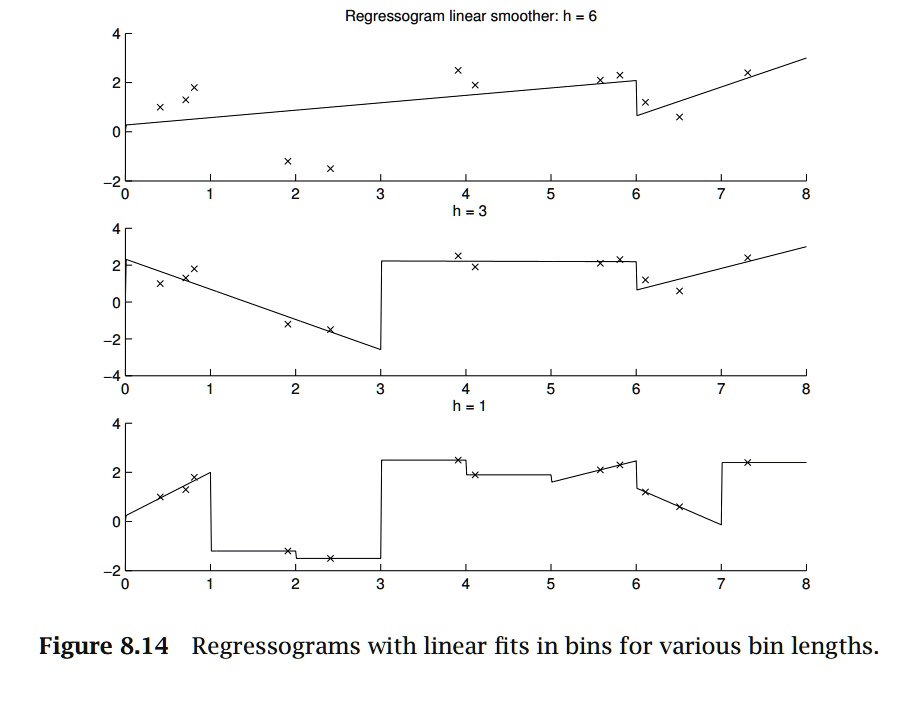
Depending on how the weights are valued and spatially arranged within the kernel, several types of linear smoothing filters can be defined. As a prelude to studying methods for bandwidth selection and other statistical inference procedures, we must first study some of the properties of linear smoothers. These usually generalize to p = 2 and p = 3, but the cod.
A clear definition of smoothing of a 1d signal from scipy cookbook shows you how it works. $$\hat{y}=s_\lambda y$$ where $s_\lambda$ is the (linear) smoother matrix. Wiggly) a smooth your data demands.
Other names given to this technique are curve fitting and low pass filtering. If you only need a line plotted summarily through a cloud of. They provide a means for smoothing noisy data.
The most familiar example is the cubic smoothing spline, but there are many other possibilities, including for the case where is. For example, in the smoothing spline problem, finally we get: A kernel smoother is a statistical technique to estimate a real valued function as the weighted average of neighboring observed data.
We’ll discuss some of the most. But how to interpret it?. Introducing the whittaker smoother, otherwise known as the perfect smoother.
For seasonal data, we might smooth out the seasonality so that we can identify the trend. The weight is defined by the kernel,.