Fantastic Info About How Do You Change Axis To Log Label X In R

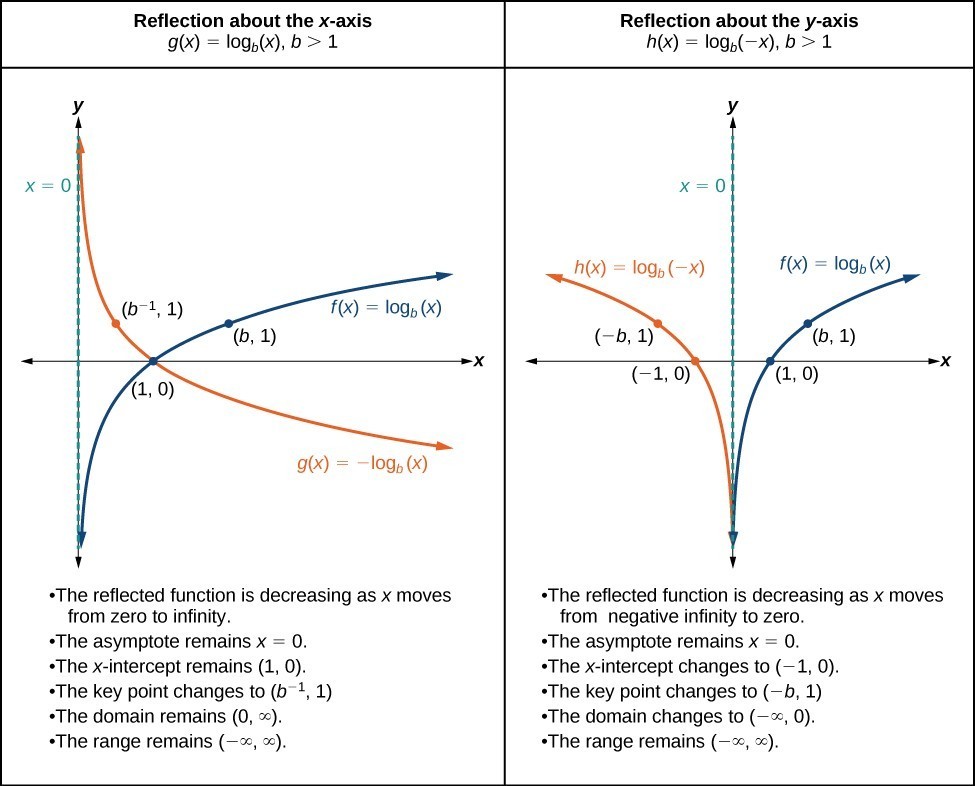
The two graphs below show the same two data sets, plotted on different axes.
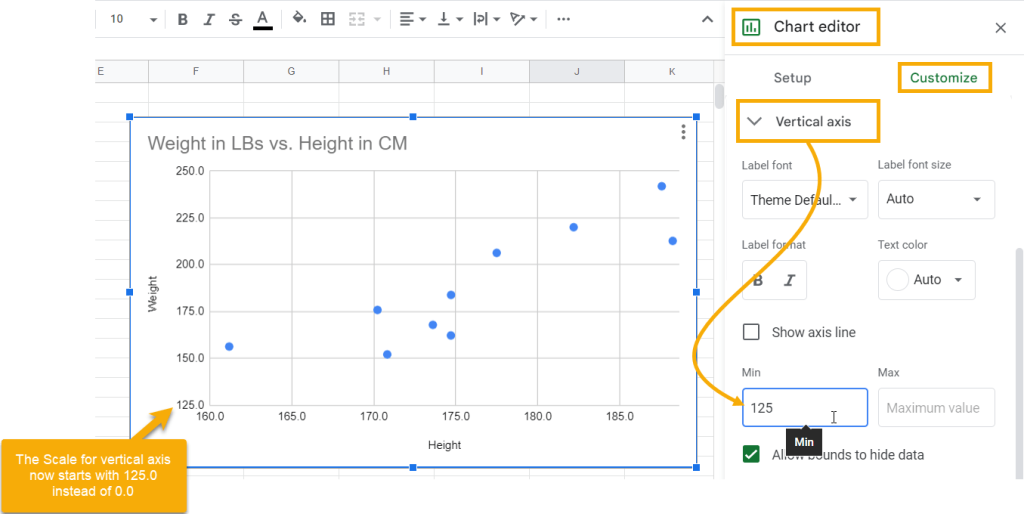
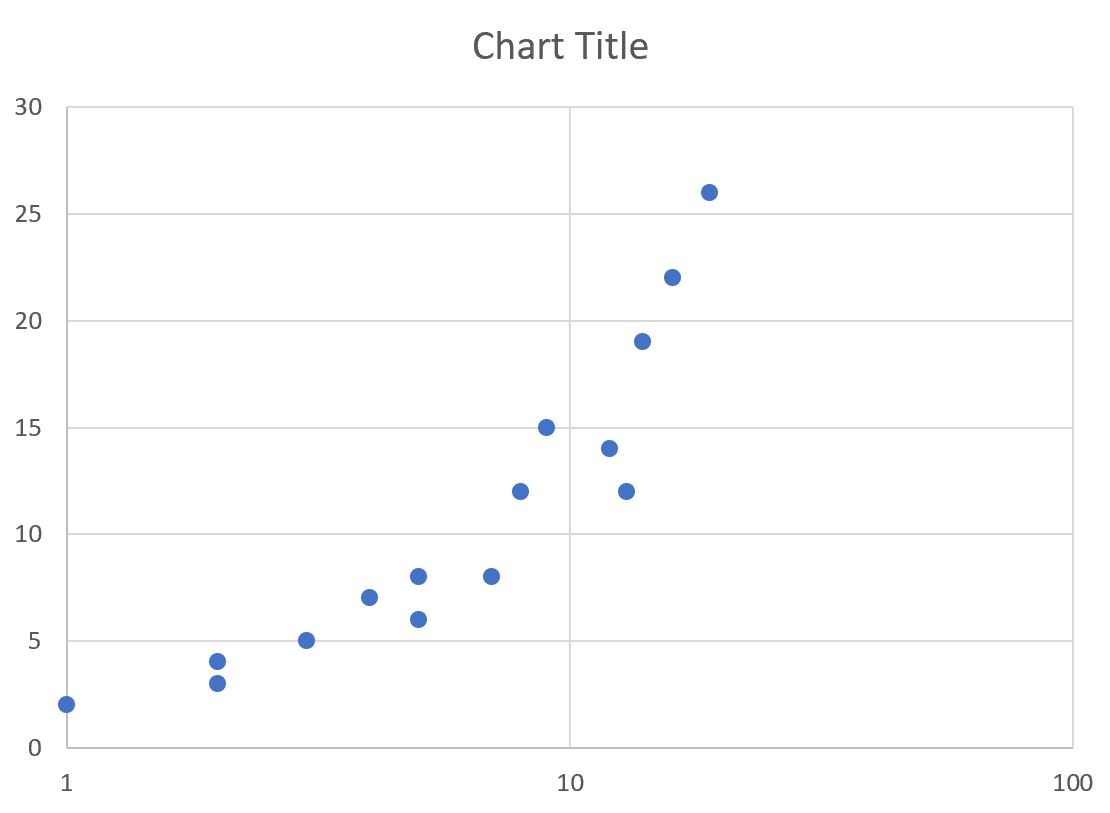
How do you change axis to log. My dataframe df is like this: The second public test realm (ptr) for diablo iv is coming soon, offering you the chance to test upcoming changes and features for season 5. You can download the workbook to learn the method.
Starting today, you’ll be able to join a discord call directly from your playstation 5 console — no mobile. How do i convert a pandas index of strings to datetime format? Following the steps in custom axis, y = 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 we can plot the logs of the data on a linear scale, from log(8) = 0.903 to log(12) = 1.079.
Our most recent general election. How to change axis scales in excel plots (with examples) by zach bobbitt january 28, 2022. While when i want to do same thing to.
Starting in r2023b, you can change the scale of any axis after you create the plot by calling the xscale, yscale, or zscale function. This will instantly transform your chart to a log. You can use the axes.set_yscale method.
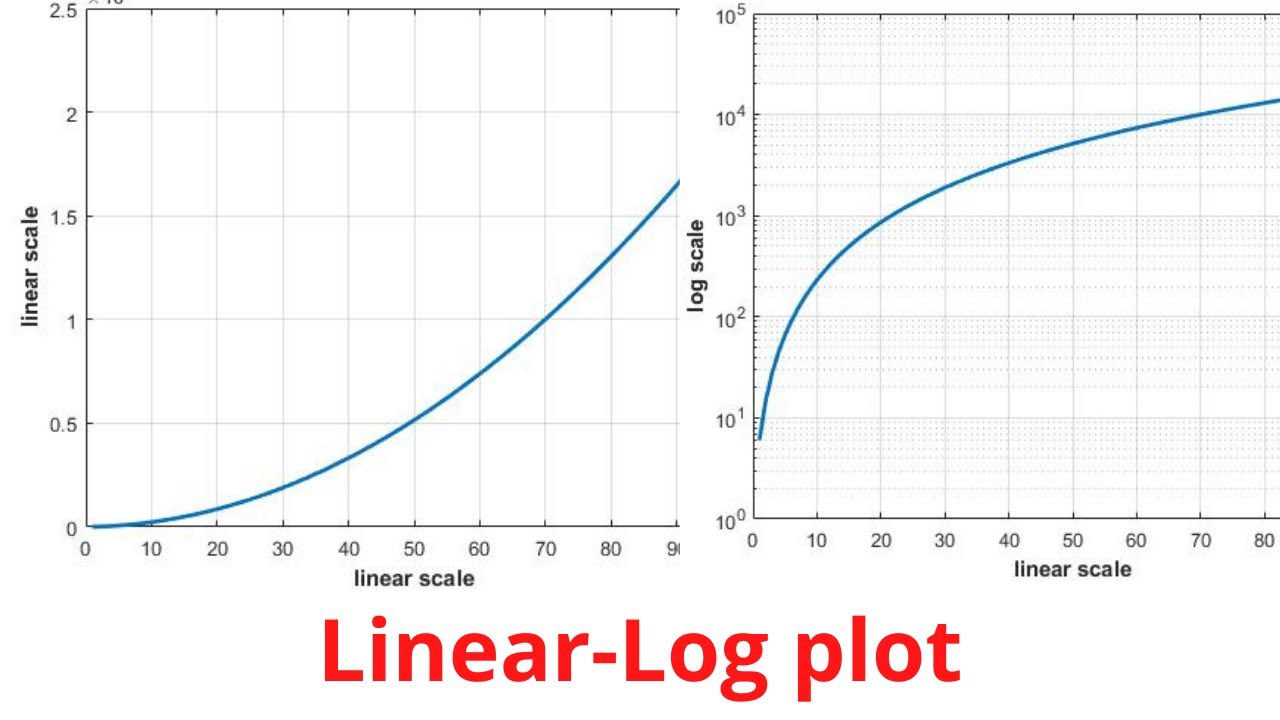
To transform your data to logs: A logarithmic axis changes the scale of an axis. The graph on the left has a linear (ordinary) axis.
It’s simple to do: For example, create a plot of two. Just select your data, go to the ‘format axis’ option, and choose the ‘logarithmic scale’ box.
Make sure you create (or change to) a xy scatter chart. Y = 2 *log10 (x) + 3 ; Create a scatter chart, change the horizontal (x) axis scale to a logarithmic scale, and change the vertical (y).
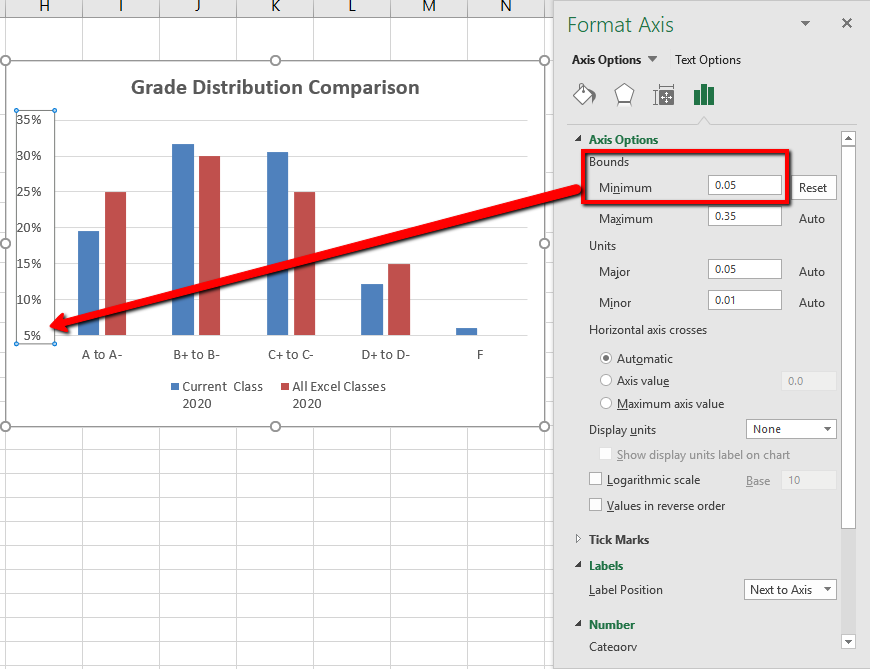
Right click on the axis numbers, select format axis, go to the number section, and enter the following custom format: When a value axis covers a very large range, you can also change the axis to a logarithmic scale (also known as log scale). We’ve got a big one to share with you:
This step applies to word for mac only: That would also allow you to build a control to let the user pick. Can i switch between a linear and logarithmic axis scale in excel?
It is crucial to notice that the dataset we will work with has some numeric values, which are remarkably less than the other values. That allows you to change the scale after the axes object is created. To illustrate this point, let’s examine a representative dataset.